Incoterms (Eng. Incoterms, International commercial terms) are rules, consolidated terms, the most widely used exceptional conditions when concluding contracts, and allowing definitions for them, requiring an unambiguous interpretation of the mandatory concepts used in the field of foreign economic activity. They determine when the risks, responsibilities and obligations of the transfer of goods by the buyer.
The main task of Incoterms is to standardize and optimize the terms of international supply contracts to bring them into line with the laws of all countries participating in the contract. Incoterms have the status of an international normative act and are published in the form of a dictionary.
The definition of common rules was one of the first initiatives of the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) after its creation in 1919.
In the early 1920s, the ICC tried to understand the trade terms used by international merchants in their transactions. The studies were carried out in 13 different countries. The conclusions were published in 1923 in the form of the first six rules, which became the forerunners of the future rules of Incoterms. The terms FAS, FOB, FOT, FOR, CIF and C&F (CNF) became them.
In 1928, a second study was carried out to study the discrepancies, the scope was expanded to the interpretation of trade terms used in more than 30 countries. Based on the results of these studies, the first version of the Incoterms rules was published in 1936, which included trade terms: FAS, FOB, C&F (CNF), CIF, EXS and EXQ.
Subsequently, a new edition of Incoterms appeared once a decade, starting from the 50s of the last century.
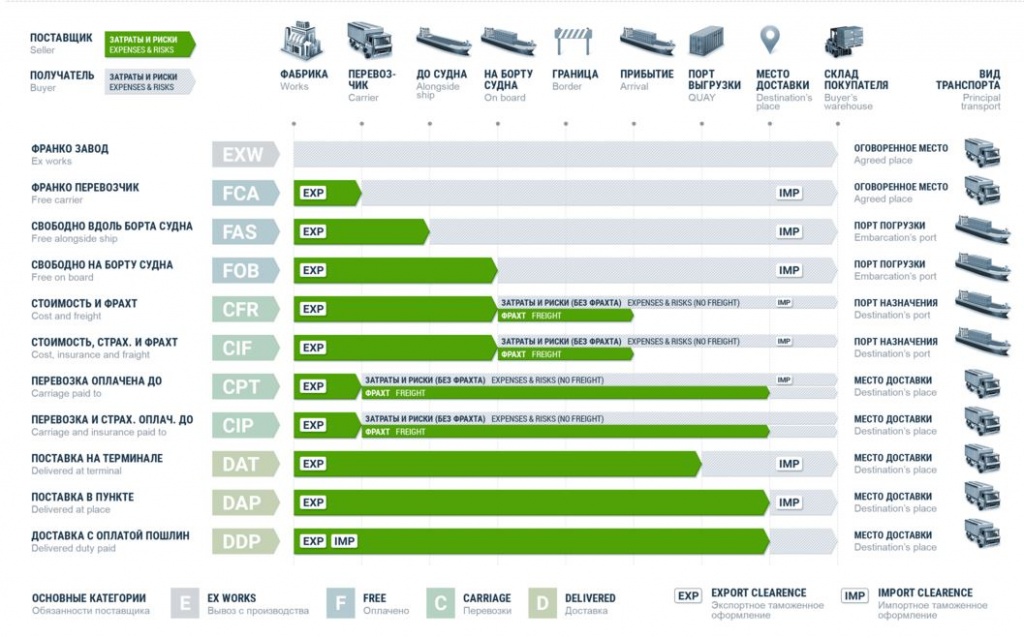
The text of the rules published in 2020 is relevant today. At the moment, there are 11 terms (divided into 4 groups) on the basis of which a foreign trade contract is drawn up.
Incoterms® Incoterms® is a registered trademark of the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). The interpretation of Incoterms on our website is not original and differs from the official translation, the copyright for the original text belongs to the International Chamber of Commerce.